Tax and government terms are, in general, coincided each other in the perception citizens. If someone tries to go into the roots of tax in concept and in practice, it has been evolved with the evolution of “the state”. The need for the state emerged by itself first for the need of people being safe. Defense was the main function of the state in its earliest form while, public works such as roads, public infrastructure and buildings had come afterwards for the responsibility of the state. Then some other functions had been linked to the state during the modern times such as health, education, public services. These needs were loaded to the state as a responsibility of governing the territory it rules. But there is a need for a way of reimbursement in order to cope with the demands of people living in a state. The reimbursement technique for the governments to finance all these works and services is called “tax”. That’s why emerging of states and the tax raising power coincided in the history of mankind. In brief, tax raising and collection is only entitled to the states but no one else. There is also a another means of taxation; it is to redistribute the wealth among the social groups to diverge the imbalance of income within the society.
There are many schemes of taxing but, in general, the taxing system is divided into two main groups: “Direct taxes” that are imputed and collected at the source of income and “Indirect taxes” that are collected during making consumption and imposed to consumers.
Direct Taxes: They are entitled to and collected from the individuals and entities when there is a revenue or income. Hence, it is a tax to be collected at the source. The liability for the direct taxes cannot be transferred to someone else and the tax accrual must be paid directly by the taxpayer to the government. Examples of the direct taxes are income tax, corporate tax and property tax. Direct taxes are said to be “progressive” which means that, as the income/revenue increases the tax liability also increases. In real life there is an incremental scheme of taxing ratio with the level of income or profit.
Indirect Taxes: They are not directly linked to the income and these taxes are aimed to be collected at the consumption. The universal example of this kind of taxes is the Value Added Tax (VAT) that is collected nearly from every item to be purchased. Sales taxes, city taxes taken from accommodation are also examples of indirect taxes. Indirect taxes are normally added to the cost of the goods or services and paid by the consumer to the vendor. The vendor collects the tax on behalf of the government. This means that indirect taxes can be transferred to other individuals or entities. And then the vendor finally pays the tax to the government on behalf of the customer. As the share of registered economy decreases, the share of indirect taxes increases in total tax revenue of any state in the global economy. This is the “trick” of the “taxman” for taxing at the consumption if not at the income!
According to the Tax Administration of Kosovo (TAK), in our country the following types of taxes are applied:
A summary of tax rates in Kosovo is represented below:
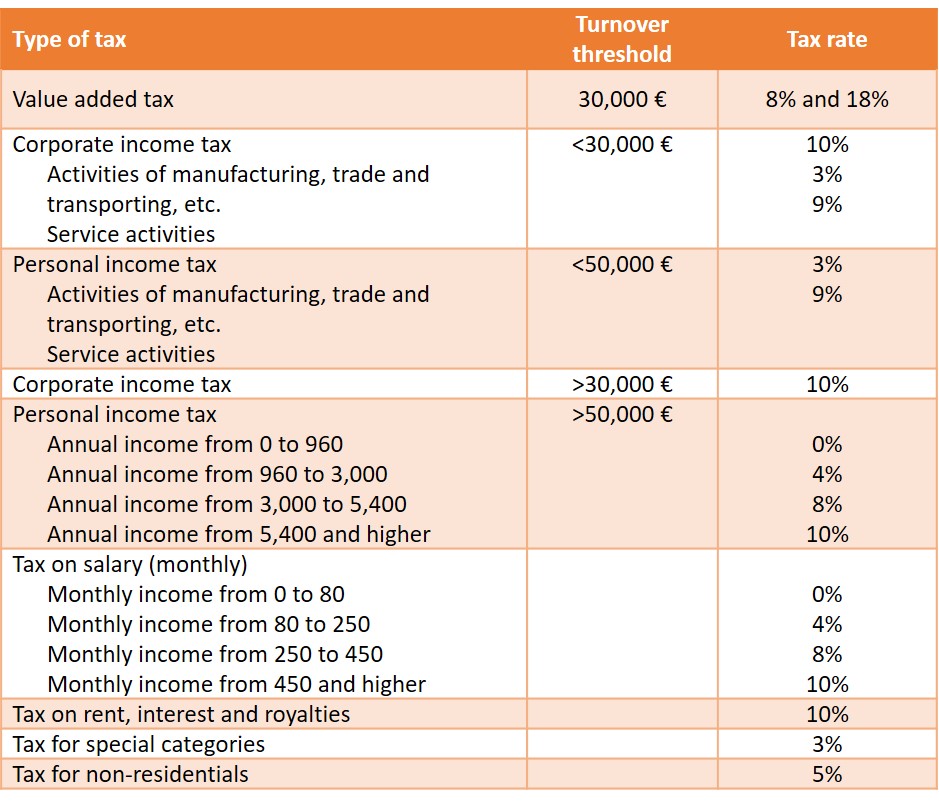
Source: Tax Administration of Kosovo
In addition to these taxes there is also social security tax on salaries and wages that is 10% (5% paid by the employee and 5% paid by the primary employer). It is the employer’s responsibility to deduct it from the income of the employee on behalf of the government and pay to the government on behalf of the employee.
The tax subject is not a well-known subject for businesses and specifically for MSME’s. But they should know it deeply in order to evade from tax liability for any means of legal opportunities and also not to be entitled for fines for improper cases.
